
China’s sprawling cities, breathtaking landscapes, and extensive highway network make driving an appealing option for many foreign visitors and residents.
However, navigating the legal requirements and understanding local driving culture can be challenging.
This comprehensive guide explains the rules, regional variations, and practical tips you need to know before getting behind the wheel in the Middle Kingdom.
Can Foreigners Drive in China?
Yes, foreigners can legally drive in China, but there are specific requirements to meet.
A crucial point to understand is that China does not recognize International Driving Permits (IDPs) or foreign licenses for direct use (China Ministry of Public Security).
Therefore, all foreign drivers must obtain either a temporary driving permit or a full Chinese driver’s license.
Types of Driver’s Licenses in China
1. Temporary Driving Permits (临时驾驶许可证)

Temporary permits are designed for short-term visitors planning to drive for less than 90 days.
Key characteristics include:
- Validity limited 90 days but can be renewed for up to 1 year
- Usually restricted to the province or city of issuance
- Available at major entry points and DMV or 车管所
- Cost: ¥200-300 depending on the region (Shanghai Traffic Police)
2. Full Chinese Driver’s License (驾驶证)
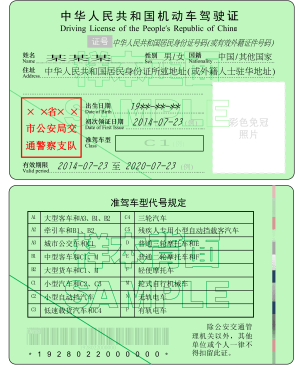
Required for long-term residents or frequent drivers, a full license involves:
- Validity of 6 years for first-time applicants
- Valid throughout mainland China
- Renewable before expiration
- Requires passing a theory test and sometimes a practical examination
- Cost: ¥300-500 including medical examination fees (Beijing Traffic Management Bureau)
Regional Variations in Driving Regulations
Driving regulations can vary significantly across China’s diverse regions:
Tier-1 Cities (Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen)
- License Plate Restrictions: These cities implement license plate lotteries or auctions to control vehicle numbers. In Beijing, the chance of winning a license plate lottery is less than 0.1% (Beijing Transport Institute)
- Driving Restrictions: Many implement odd-even license plate driving days during high pollution periods
- Electric Vehicle Incentives: Preferential policies for EV registration and usage
Tier-2 Cities
- Generally less restrictive licensing requirements
- Some cities like Hangzhou and Tianjin have begun implementing similar restrictions to tier-1 cities
- More accessible parking and less congestion
Rural Areas
- Fewer traffic cameras and enforcement mechanisms
- Road conditions may vary significantly
- Limited access to vehicle services and charging infrastructure
How to Apply for a Temporary Driving Permit
For visitors staying less than 90 days, here’s the process:
- Locate the Appropriate Office
- Major airports (Beijing Capital, Shanghai Pudong, Guangzhou Baiyun)
- Local Vehicle Administration Offices (车管所)
- Some high-end hotels and rental agencies can assist with applications
- Required Documents
- Valid passport with Chinese visa
- Original driver’s license from your home country
- Certified Chinese translation of your license (must be done by an authorized translation service)
- 2-3 color passport-sized photographs (2 inches)
- Completed application form (available at the office)
- Processing Time and Collection
- Same-day processing in most locations
- Some remote areas may require 2-3 business days
Obtaining a Full Chinese Driver’s License
For expats and long-term residents, follow these detailed steps:
Step 1: Document Preparation
- Valid passport with residence permit (work visa, student visa, or other long-term visa)
- Original foreign driver’s license
- Notarized and authenticated Chinese translation of your license (costs approximately ¥300-500)
- Proof of residence (housing registration form or lease agreement)
- 4 recent passport-sized photographs with white background
- Completed application form (available here)
Step 2: Medical Examination
- Visit a designated medical center (usually located near the Vehicle Administration Office)
- Tests include vision, color recognition, and reaction time
- Cost: approximately ¥100-150
- Results are typically provided immediately
Step 3: Theory Test
The computerized theory test consists of 100 multiple-choice questions covering:
- Traffic laws and regulations
- Road signs and markings
- Safe driving practices
- Emergency procedures
Important Notes:
- Available in multiple languages including English, Japanese, Korean, and Arabic
- Passing score is 90/100
- Time limit: 45 minutes
- Study materials available at the testing center or online (Official practice tests)
- Test fee: approximately ¥50
Step 4: Practical Driving Test (If Required)
Some applicants may need to take a practical driving test if:
- Your foreign license is less than 1 year old
- Your license doesn’t have a clear issuance date
- The authenticity of your license cannot be verified
The practical test includes:
- Basic vehicle operation
- Parking maneuvers
- Road driving assessment
- Cost: approximately ¥200-300
Step 5: License Issuance
- Processing time: 1-2 weeks in major cities, up to 1 month in smaller cities
- Collection requires your original passport
- License validity: 6 years for first-time applicants
Road Rules and Regulations
Basic Traffic Rules
- Drive on the right side of the road
- Seatbelts mandatory for all passengers
- Mobile phone use while driving prohibited (¥200 fine and 2 points on license)
- Child safety seats required for children under 4 years (National Safety Regulation GB 27887-2011)
Speed Limits
- Urban areas: 30-60 km/h (18-37 mph)
- Provincial roads: 60-80 km/h (37-50 mph)
- Expressways: 80-120 km/h (50-75 mph)
- School zones: 30 km/h (18 mph)
Traffic Violation Point System
China uses a 12-point system for traffic violations:
- Accumulating 12 points within 12 months requires retaking the theory test
- Serious violations can result in immediate license suspension
- Points reset after 12 months
- Common violations and associated points are listed on the National Traffic Management Bureau website
Vehicle Rentals for Foreign Drivers
Major Rental Companies
- International: Hertz, Avis, Enterprise (Hertz China)
- Domestic: eHi Car Services, China Auto Rental (CAR Inc)
Rental Requirements
- Valid Chinese driver’s license or temporary permit
- Passport and visa
- Credit card for deposit (typically ¥2,000-5,000)
- Minimum age requirement: usually 22-25 years
- Minimum driving experience: 1-2 years
Insurance Options
- Basic insurance (included in rental): Covers basic liability
- Comprehensive insurance (recommended): Covers damage to the vehicle
- Personal accident insurance: Covers medical expenses
- Third-party liability insurance: Mandatory by law
Electronic Toll Collection (ETC) System
China’s expressways use an electronic toll collection system:
- ETC devices can be rented with your vehicle
- Most rental cars come pre-equipped
- Toll rates vary by vehicle type and distance
- Payment is automatically deducted from a linked account
- National ETC Service Platform provides coverage maps and rate information
Essential Driving Apps and Technology
Navigation Apps
- Baidu Maps (百度地图): Most accurate for mainland China, includes real-time traffic (Download)
- AutoNavi/Gaode (高德地图): Owned by Alibaba, excellent for urban navigation (Download)
- Apple Maps: Improved coverage in China but less detailed than local options
Traffic and Parking Apps
- Tingchebao (停车宝): Helps find parking spaces in major cities (Download)
- Didi Parking (滴滴停车): Integrated with China’s largest ride-sharing platform (Download)
Translation Apps
- Baidu Translate: Useful for road signs and communication with traffic police
- WeChat: Built-in translation feature for communication emergencies
Common Driving Challenges and Solutions
Traffic Congestion
Major cities experience severe congestion, particularly during rush hours (7-9 AM, 5-7 PM):
- Use navigation apps with real-time traffic updates
- Consider public transportation for inner-city travel
- Many cities have traffic restriction days based on license plate numbers
Language Barrier
- Keep a digital translator handy
- Learn basic Chinese phrases related to driving and emergencies
- Carry a card with your destination written in Chinese
- Save your hotel address in Chinese characters
Unique Driving Behaviors
- Expect frequent lane changes without signaling
- Pedestrians and cyclists may cross unexpectedly
- Honking is common and not necessarily aggressive
- Maintain defensive driving practices at all times
What to Do in Case of an Accident
- Stop immediately and turn on hazard lights
- Call the police (110) and ambulance if needed (120)
- Document the scene with photographs
- Exchange information with other parties involved
- Contact your insurance provider
- Do not admit fault or sign any documents you don’t understand
- Request a police report (交通事故认定书) – essential for insurance claims
For serious accidents, contact your embassy or consulate (List of Foreign Embassies in China)
Real Experiences from Expat Drivers
“The theory test was challenging, but studying the practice questions helped immensely. The biggest adjustment was getting used to the aggressive driving style in Beijing.” – Michael, American expat, 3 years in China
“In Shanghai, I found the electronic toll system very convenient, but navigating the license plate restrictions was confusing at first. Local colleagues helped me understand the system.” – Sophie, French expat, 2 years in China
“Driving in smaller cities like Kunming was much easier than I expected. Less congestion and more relaxed enforcement of rules, though road conditions varied significantly.” – James, Australian expat, 4 years in China
Electric Vehicle Considerations
China leads the world in electric vehicle adoption, with special considerations for EV drivers:
- Charging Infrastructure: Over 1.3 million public charging stations nationwide (China Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Promotion Alliance)
- Preferential Policies: Many cities offer free or preferential parking for EVs
- License Plate Advantages: EVs often exempt from license plate lotteries or auctions
- Range Considerations: Plan longer trips carefully as rural charging infrastructure may be limited
Resources for Further Information
Official Government Resources
- China Ministry of Public Security – Traffic Management Bureau
- National Transportation Safety Committee
- China Road Traffic Safety Association
Driving Schools for Foreigners
- International Driving School Beijing
- Shanghai Foreign Drivers Training Center
- Guangzhou Expat Driving Academy
Expat Forums and Resources
Conclusion
Driving in China offers unparalleled freedom to explore this vast and diverse country, but requires careful preparation and understanding of local regulations.
By obtaining the proper documentation, familiarizing yourself with regional variations, and adopting defensive driving practices, you can navigate China’s roads safely and confidently.
Remember that regulations change frequently, so always verify current requirements with official sources before planning your journey.
Safe travels on the roads of the Middle Kingdom!
This guide is updated regularly to reflect the latest changes in China’s driving regulations. Last verified: February 2025.


